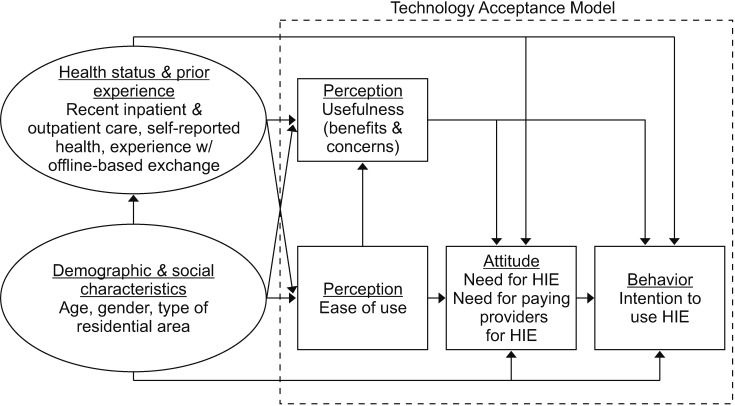
1. The Characteristics of the Sample and the Validity and Reliability of the Survey Instrument
The general characteristics of the study sample are presented in
Table 1. The age distribution and the type of residential area distribution approximately reflected the distributions of the population [
26]. Fifty-five percent of the study sample had experience with offline-based health information exchange, such as carrying hardcopies of medical records and diagnostic images stored on a compact disk or USB drive.
The results of the analyses executed to examine the validity and internal consistency of the survey instrument are presented in
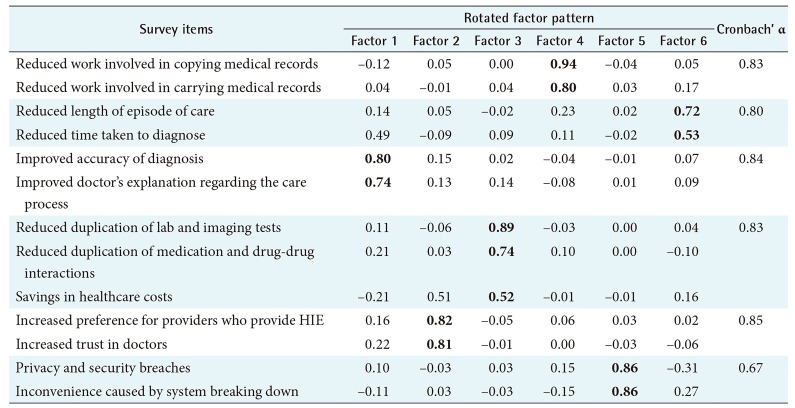
Table 2. The exploratory factor analysis grouped 13 questions included in the questionnaire to assess the PU of HIE into six factors, which represented the attributes of benefits and concerns of HIE. There were five factors for benefits-improvement in diagnosis accuracy and doctors' communication regarding care processes, improvement in provider-patient relations, decrease in duplication of care and healthcare costs, convenience of HIE by reducing the burden related to health information exchange, and expedited care process. There was one factor for concerns, namely, privacy breaches and system break down. All factor loadings were over 0.5, and Kaiser's measure of sampling adequacy (MSA) was 0.91, which indicated that the analysis results fit well. Cronbach's alpha coefficients, which reflect how well a group of items asked differently for an attribute focuses on the attribute consistently, were mostly over 0.70, which is used as a threshold for acceptable values. We defined six variables to measure the attributes of PU of HIE based on the analysis results.
2. Public Acceptance of HIE
Descriptive statistics of responses to the questions included in the survey to assess the constructs of TAM are presented in
Table 3. The average level of agreement regarding the ease of use of HIE technology was 3.2, which is a little higher than the neutral level. The average levels of agreement for the questions concerning benefits of HIE ranged from 3.76 to 4.49. Respondents agreed most highly with the statements that HIE would reduce the burden of copying and carrying medical records, which is an intrinsic function of HIE (4.49 and 4.38). The next highest agreement was found for the statements that HIE would expedite care processes by reducing the time required for diagnosis (4.32 and 4.30). Then, the statements regarding the reduction of duplicated medication and adverse drug interactions and the reduction of duplicated tests followed (4.29 and 4.25). The levels of agreement concerning the benefits of improved doctor-patient communication, reduction of healthcare costs, and improved diagnosis accuracy were lower in comparison to other benefits (4.0, 3.99, and 3.95). The statements for which there was least agreement were about provider-patient relations with averages of 3.84 and 3.76. The levels of agreement with the statements concerning adverse effects of the technology were between the levels of ‘neutral’ and ‘agree’ (3.69 and 3.46).
The respondents' acceptance of the technology was high. The average level of agreement with the need for HIE was 4.16, and 87% of the respondents expressed their intention to use HIE. However, the respondents were not enthusiastic about paying providers for provision of the service. The average was 3.04 which is right at the neutral level.
3. Factors Influencing Public Acceptance
Descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation coefficients between variables are presented in
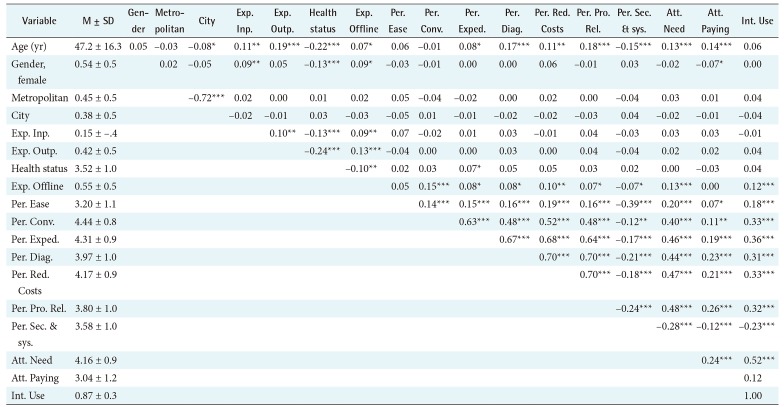
Table 4. Age was correlated with most variables in the model with varying degrees of significance except for the intention to use HIE, PEOU, and the convenience benefit. Experience with offline-based information exchange was significantly correlated mostly with perception, attitude, and intention variables except for the PEOU and the attitude about paying providers for HIE. The perception, attitude, and intention variables were positively correlated with each other with a high degree of significance except for the perception of the concern about the technology, which showed significant negative correlations.
Coefficient estimates of SEM are presented in
Table 5. The log-likelihood of the fitted model, the Akaike information criterion (AIC), and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) were −15,062, 30,440, and 31,210, respectively.
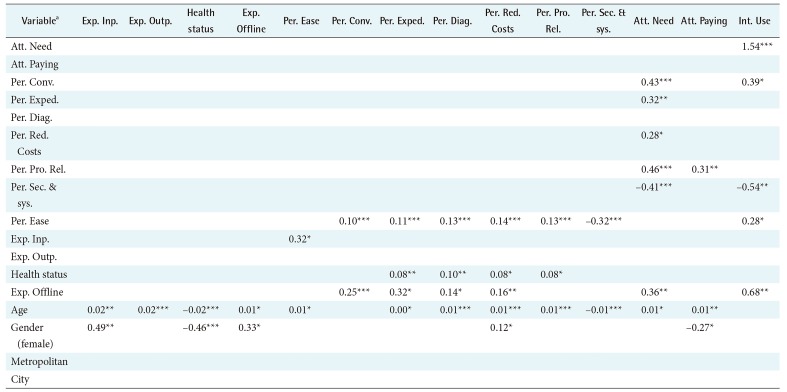
The variable with the largest positive influence on the intention to use HIE was the attitude towards the need for the technology (coefficient estimate = 1.54, p < 0.0001). The results indicate that the odds for choosing to use HIE increased by 366% as the level of agreement with the statement regarding the need increased by one when all other variables were held at a fixed value. The variable with the second largest influence was prior experience with offline-based information exchange. The odds of choosing to use the technology for respondents with such experience were 97% higher than those without such experience (p < 0.01). Perception about the convenience benefit of the technology had a positive direct influence on the intention to use (coefficient estimate = 0.39, p < 0.05) and a positive indirect influence through the influence on the attitude towards the need for the technology. The PEOU of the technology had a positive direct influence on the intention to use (coefficient estimate = 0.28, p < 0.05) and had positive indirect influences through the positive influences on perceptions of convenience, expedited care process, reduced care duplications and costs, and improved provider-patient relations benefits. The perception about the concerns of information security and system reliability negatively influenced the intention to use (coefficient estimate = −0.54, p < 0.01). The odds of choosing to use HIE decreased by 42% as the value of the variable increased by one with all other variables held at a fixed value.
The attitude towards the need for HIE was directly positively influenced by the perception of technology benefits: convenience (0.43, p < 0.0001), expedited care process (0.32, p < 0.01), reduced duplication of care and costs (0.28, p < 0.05), and improved provider-patient relations (0.46, p < 0.001). It was negatively influenced by the perception of technology concern: security breaches and system break down (−0.41, p < 0.0001). Also prior experience with offline-based information exchange and age influenced attitude positively (0.36, p < 0.01 and 0.01, p < 0.05, respectively). However, attitude was not directly influenced by the PEOU; rather, it was indirectly influenced by the PEOU through the perception of benefits and concerns of the technology. Variables with a direct positive influence on the positive attitude towards paying providers for the service provision were the perception of provider-patient relations benefit and age (0.31, p < 0.01 and 0.01, p < 0.01, respectively). Also, female respondents were less likely to agree with paying providers for HIE (−0.27, p < 0.05).
All attributes of PU of HIE were significantly influenced by the PEOU of the technology as TAM posited. The directions of the influences of benefits were positive, whereas the perception of concerns had a negative influence. As the level of agreement with the statement regarding the PEOU of HIE increased by one, the levels of agreement with the statements regarding convenience, expedited care process, improvement in diagnosis and communication, reduced duplication of care and healthcare costs, and improvement of provider-patient relations increased by 0.1, 0.11, 0.13, 0.14, and 0.13, respectively (all significant at p < 0.0001). The level of agreement with the statement regarding information security and system reliability concerns deceased by 0.32 (p < 0.0001) as the level of agreement with the statement regarding PEOU increased by one. Self-reported health status, prior experience with offline-based information exchange, and age also directly influenced the PU of HIE. Respondents' concern about information safety and system reliability decreased as age increased (−0.01, p < 0.0001). Respondents who had inpatient care in the previous year had a higher level of agreement with the statement about PEOU (0.32, p < 0.0001), and age influenced PEOU positively (0.01, p < 0.05).
Age directly and indirectly influenced the constructs of TAM: perceptions, attitudes, and intention. Age was also significantly associated with the control variables that we included in the model to measure health status and previous experience with offline-based information exchange. The probability of having inpatient care in the previous year increased by 1.85% (p < 0.01), having outpatient care in the past two weeks increased by 2.51% (p < 0.0001), having self-reported health status decreased by one level increased by 2.36% (p < 0.0001), and having offline-based information exchange increased by 0.87% (p < 0.01) as age increased by one and all other variables were held at a fixed value. The probability of having inpatient care in the previous year for female respondents was 63.55% higher than for male respondents (p < 0.01). Female respondents' odds of selfreported health status increasing by one level (direction for better health) was 36.57% smaller than for male respondents (p < 0.0001) and having offline-based information exchange was 39.32% larger (p < 0.05). The type of residential area did not influence any of the variables in the model.
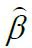 is coefficient estimate.
is coefficient estimate.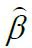 is coefficient estimate.
is coefficient estimate.