I. Introduction
As analyses based on clinical medical data can be used as clinical decision support to help experts make decisions, this technique has been extensively used by researchers in recent studies [
1,
2]. In particular, clinical documents, which are included in Electronic Medical Records, contain important data because these documents are written by clinical experts. In fact, in the field of medical services, clinical documents have been analyzed, and relevant data have been extracted and used for important decision-making, such as text summarization, automatic question-and-answer systems, dialog systems, and machine translation [
3].
However, these clinical documents are limited in terms of their secondary use because protected health information (PHI) is included in clinical documents, including patients’ personal and sensitive information. Therefore, to ensure confidentiality, these types of PHI must be de-identified [
4]. In particular, the Health Insurance Portability and Account-ability Act (HIPAA) [
5] in the United States defined guidelines for the secondary use of medical records and the de-identification of medical records. Until all types of PHI have been de-identified, clinical documents are not available to the public.
Thus, identifying, removing, and de-identifying PHI is crucial as it allows more researchers to access clinical data and encourages the secondary use of these data. In particular, the existing PHI de-identification process has been performed only by humans. A medical records specialist directly identifies and removes the PHI from clinical documents, but this method is costly and time-consuming.
Research on generalized PHI identification algorithms to help reduce human effort is ongoing. In particular, knowledge- and rule-based methods have been widely used as automatic identification algorithms. A knowledge-based system can be implemented using an algorithm that creates a word dictionary and finds words therein. Meanwhile, a rule-based system uses a set rule to recognize formatted text, such as phone numbers or URLs, mainly using regular expressions. Thus, Shin et al. [
6] proposed a de-identification method using regular expressions in clinical documents in Korea.
However, a limitation of knowledge- and rule-based systems is that they cannot recognize new forms of PHI that are different from a set form or rule. Deep learning models are more likely to recognize PHI than traditional methods. Specifically, clinical documents involve many abbreviations and typos. Furthermore, since the forms to be filled out for each clinical expert vary, using prescribed rules or a dictionary of words is challenging. Therefore, machine learning-based PHI identification methods have been proposed. In particular, the conditional random field (CRF) method [
7] received attention because it exhibited effective PHI recognition performance by directly using the context, consisting of the front and back of the words. Lafferty et al. [
8] showed that the F1-score of rule-based PHI recognition of individual entities in clinical documents was 64.12%, but a substantially higher performance of 81.48% was obtained using CRF.
As part of machine learning-based methods, deep learning-based methods based on artificial neural networks [
9] are also being actively considered. Deep learning can be used to construct an advanced model by automatically extracting features without the precise feature engineering required by machine learning. In particular, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) [
10] are used to solve problems through real-time recursive training that can utilize previously acquired information to solve a current problem. In addition, long short-term memory (LSTM) [
11] is a model made by improving the RNN and can grasp contexts by considering previous data. In their study that used LSTM, Liu et al. [
12] achieved a high PHI recognition performance.
Pre-training-based models are being actively investigated to effectively perform these tasks as part of natural language processing. Furthermore, methods such as Word2Vec [
13], fastText [
14], and ELMo [
15] are pre-trained with a large amount of data to pre-configure the embedding vector. These pre-trained models can be applied to new projects to improve their performance. LSTM, which exhibited superior performance in the existing natural language processing field, achieved higher performance than the existing training model that used Word2Vec [
16].
Specifically, the bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) method, developed by Google, has attracted attention because it is trained with contextual principles and can be fine-tuned in various fields. Unlike the existing model, BERT uses masking, which randomly masks and predicts the token that should be predicted. Satisfactory performance was obtained using this method, and various derivative models based on the BERT were released.
Therefore, in this study, a pre-trained model was used to improve the effectiveness of PHI recognition performance. Thus, we propose a model for recognizing various types of PHI contained in clinical documents using BERT, the robustly optimized BERT pre-training approach (RoBERTa), and XLNet (a model built based on Transformer-XL). We tested our methodology using open datasets for performance comparisons.
II. Methods
Figure 1 shows a comparison of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet to verify PHI recognition performance. The letters in the clinical document were tokenized and identified by inside-outside-beginning (IOB) tagging. Subsequently, the tagged letters were tokenized through WordPiece tokenization to create inputs that can be placed into each pre-training model. The resulting data were trained with BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet and evaluated to determine the performance of the models. The pipeline was tested on the i2b2 2014 dataset.
1. Experimental Data
The i2b2 2014 dataset was used in this study [
17]. This is one of the most representative datasets publicly available for recognizing PHI in clinical documents. This dataset consists of 1,304 anonymized medical records of 296 patients with diabetes. To revitalize de-identification research in the medical field, the Clinical Natural Language Processing Challenge was conducted at i2b2 2014, and in this study, a dataset that was part of the challenge was used. In total, 790 data records from 188 patients were provided for training, and 514 data records from 109 patients were used for testing. Furthermore, 17,045 PHI instances for training and 11,462 PHI instances for testing were provided as annotated into seven large categories and 25 detailed categories. Further, it can be used with permission from the i2b2 homepage [
18]. The PHI included in the dataset was directly annotated by a medical records specialist and was annotated based on the HIPPA-PHI category and the more detailed i2b2-PHI category, as follows:
NAME (types: PATIENT, DOCTOR, USERNAME)
PROFESSION
LOCATION (types: ROOM, DEPARTMENT, HOSPITAL, ORGANIZATION, STREET, CITY, STATE, COUNTRY, ZIP, OTHER)
AGE
DATE
CONTACT (types: PHONE, FAX, EMAIL, URL, IP ADDRESS)
IDs (types: SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER, MEDICAL RECORD NUMBER, HEALTH PLAN NUMBER, ACCOUNT NUMBER, LICENSE NUMBER, VEHICLE ID, DEVICE ID, BIOMETRIC ID, ID NUMBER)
2. Preprocessing
Appropriate preprocessing must be performed to input sentences into the deep learning model. We tokenized words and identified them using an IOB tagging scheme. IOB tagging is a method for recognizing entity names in named-entity recognition (NER), where “B” denotes beginning, “I” indicates inside, and “O” denotes outside. Specifically, “B” is the part where the entity name begins, “I” is the inner part of the entity name, and “O” is the part that is not the entity name. For example, in the i2b2 dataset, “record” is a meaningless word, so it is marked with O; “Frank” is the beginning of a doctor’s name, so B-DOCTOR; and “T.” is tagged as I-DOCTOR because it denotes the middle of the doctor’s name.
In addition, because BERT has a maximum input size of 512 words, each sentence is divided into 250 words and used as the model input. We set the input size to 250 given the model training time and computing environment conditions. For input into the BERT model, we tokenized the data again using the WordPiece tokenizer. WordPiece represents words in subword units until they can be represented. When tokenizing WordPiece, the beginning and end of a sentence are marked with “CLS” and “SEP” tags, respectively. To maintain the IOB tagging, it was applied equally to the token before being divided and then after.
3. PHI Recognition Model
In this study, the performance of the BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet models was compared using pre-training models. All models used in this study belong to the latest technology and are transformer-based models. BERT, a transformer-based model, has recently shown good performance, and many derivative models have been released, so we wanted to compare them.
1) BERT
BERT [
19] is a transformer-based pre-training language model developed by Google. Pre-training refers to a model that trains data in advance through masking or unsupervised learning. If pre-training is used, a higher performance can be expected because it can be fine-tuned according to the purpose. The transformer has an encoder comprising multi-head self-attention that can process information in various dimensions. Previous models, such as RNN and LSTM, have poor performance as they were mainly trained by considering all tokens. BERT, which has addressed this problem, is based on a bidirectional transformer and learns by grasping all the flow of context through multi-head self-attention. It changes layers and can be applied to various recognition tasks [
20].
In this study, the pre-trained BERT was fine-tuned and applied using the i2b2 data.
Figure 2 shows a picture of the BERT structure and explains the fine-tuned structure of the i2b2 dataset. In this study, among the BERT models, the weighting for pre-trained models “BERT-based-model (uncased)” [
19], which is a pre-trained model for English, was used.
2) RoBERTa
RoBERTa [
21] is a model released at Washington University and Facebook in July 2019, and it complements the training process of BERT. The improvements in RoBERTa can be classified into dynamic masking, input format, and large batch training.
Dynamic masking is a method for transforming the mask at every training step, unlike iterative masking in the BERT model. The mask should be dynamically transformed to analyze it using a large amount of data.
The weighting for pre-trained models “roberta-base-squad2” [
22] provided by deepset was used for fine-tuning. The Adam optimizer [
23] was used to train the model, and the training was repeated for five epochs.
3) XLNet
XLNet [
24] is a model released by Google that recorded the highest performance among 20 natural language processing datasets at the time of publication. It is a model built based on Transformer-XL and is a pre-training model based on an autoregressive and autoencoding permutation model, which is generally known to have satisfactory performance (
Figure 3).
Transformer-XL solves the shortcomings wherein the sentence length is fixed and information cannot be transmitted between segments because the existing transformer only sees the sentences once. Further, it has the advantage of containing all the information of the segment in a cache and calculating it quickly by the segment unit.
In this study, the weighting for pre-trained models “xlnet-base-cased” [
25] was used in the experiment. It consists of 12 layers and 768 hidden layers. The Adam optimizer was used for training model, and training was repeated for five epochs.
4. Evaluation
The performance of the models was evaluated in terms of recall, precision, and the F1-score. Accuracy was excluded because the amount of O (no meaning) during IOB tagging was meaningless in clinical documents, which contain a large amount of unbalanced data.
Recall recognizes that the “true” answer is indeed the correct answer, and the formula is as expressed follows:
Precision refers to identifying the correct answer among the predictions, and the formula is expressed as follows:
The F1-score [
26] is the harmonic average of precision and recall, and the formula is expressed as follows:
In this formula, true positive (TP) denotes a correct answer, a false negative (FN) is a case in which “true” is predicted as “false,” and a false positive (FP) is a case in which “false” is predicted as “true.”
III. Results
In this study, the values of recall, precision, and F1-score of each prediction model were checked to compare their performance.
1. Performance Comparison of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet
Table 1 shows the average predicted values for precision, recall, and the F1-score of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet. As presented in
Table 1, the overall performance of RoBERTa and XLNet was higher than that of the existing BERT. Further, XLNet showed the highest performance in the PHI recognition experiment with a recall of 95.82%, precision of 96.76%, and F1-score of 96.29%.
Table 2 shows the training time of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet. In BERT, training time was the shortest at 348 seconds, while the longest training time was found for XLNet, at 1,215 seconds.
2. PHI Entity Tag Performance of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet
Table 3 presents the PHI entity performance for BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet. It was observed that the recognition performance of PHI-related words, such as DOCTOR, PATIENT, and HOSPITAL, was approximately 30% higher in RoBERTa and XLNet than in BERT.
IV. Discussion
Several recent studies have focused on the use of “dark data,” and this need has emerged in the medical field, where research is being concentrated [
27]. The term “dark data” refers to data that have been collected, but only stored and are not used for analysis. In the medical field, clinical documents prepared by clinicians belong to this category. However, with recent advances in NER research, de-identification is being performed to ensure that clinical documents, which are semi-structured data, can be actively used for analysis. As research is actively conducted, efforts are being made to develop a model with better performance and a shorter training duration.
We also identified values for FP and FN as part of the performance evaluation. An example of an FP would be the prediction of an entity as DOCTOR when it was actually PATIENT. In addition, as shown in
Table 4, there were cases where the prediction was HOSPITAL, but in reality it was CITY or COUNTRY. Similarly, for FN results, there was a problem in that it was not possible to distinguish and predict similar types of data. To address these limitations, future studies will use a pre-trained model with a large amount of clinical data.
The difference between this study and other studies is that the present study adopted a pre-training model and transfer training method to develop the most effective PHI recognition model despite limited data. In particular, in the image field, various problems have been solved using pre-trained models, such as VGG, ResNET, and their weights. We applied the transfer training method for a pre-trained model to identify PHI in clinical documents and confirmed the strong recognition performance of the method.
In addition to BERT, we applied the most representative pre-training model and the latest derivative models, and we determined which model had a superior performance. In particular, XLNet showed a 10% performance improvement compared to the BERT-based model. This is because the two-stream self-attention method, which is a characteristic of XLNet, solves the change in the order of tokens due to the permutation model; therefore, it is better composed as a word embedding method than BERT.
When verifying the PHI recognition performance, RoBERTa and XLNet showed a performance improvement of approximately 30% in words related to proper nouns, such as DOCTOR, PATIENT, and HOSPITAL. This result implies that RoBERTa and XLNet are more effective in grasping the context than the general BERT model. However, for DEVICE, LOCATION-OTHER, ORGANIZATION, USERNAME, and COUNTRY, the recall, precision, and F1-score were 0. The above-mentioned entities have fewer than 200 classes, which is too small compared to other entities, so sufficient data for learning have not been secured. The absolute number of entities also affected the occurrence of this problem, but it is considered that this problem occurred because the dataset was unbalanced, with a clear difference compared to the other entity counts.
Oversampling is a method to solve data imbalance. There are deep learning methods such as variational autoencoders [
28] and generative adversarial networks [
29] for overs-ampling, and if the above methods are applied in future research, good results can be expected even for entities with poor learning rates.
A limitation of this study is that a single-institution dataset was used and that only one dataset was used. In addition, the i2b2 2014 dataset has refined data in which abbreviations and uppercase and lowercase letters are not arranged. In future research, we will conduct research that more closely reflects the characteristics of real-world medical documents using multi-institutional medical document datasets.
In this study, we compared the prediction performance of the three models, namely, BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet, which are pre-training models that have recently been used. The performance of XLNet was superior among these three models. A model that had been pre-trained using a general corpus was used; however, in previous studies, the BERT model was trained to specialize in various documents and exhibited satisfactory performance [
30]. In future studies, better performance can be achieved if a model that has been pre-trained with clinical and biomedical documents, among others, is used.
Another limitation of this study is the problem of generalizing the model. There are few publicly available PHI data-sets that are properly annotated, making it difficult to apply a model to many datasets. Further, the i2b2 dataset, which was used to verify this model, has a single data format from a single institution. Therefore, future research will focus on collecting multi-center and various types of clinical documents and presenting a more generalized model.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea, under the Information Technology Research Center support program (No. IITP-2021-2017-0-01630) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion).
Figure 1
Pipeline showing the inputs and outputs of deep learning models: BERT (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers), RoBERTa (robustly optimized BERT pre-training approach), and XLNet (a model built based on Transformer-XL). IOB: inside-outside-beginning.
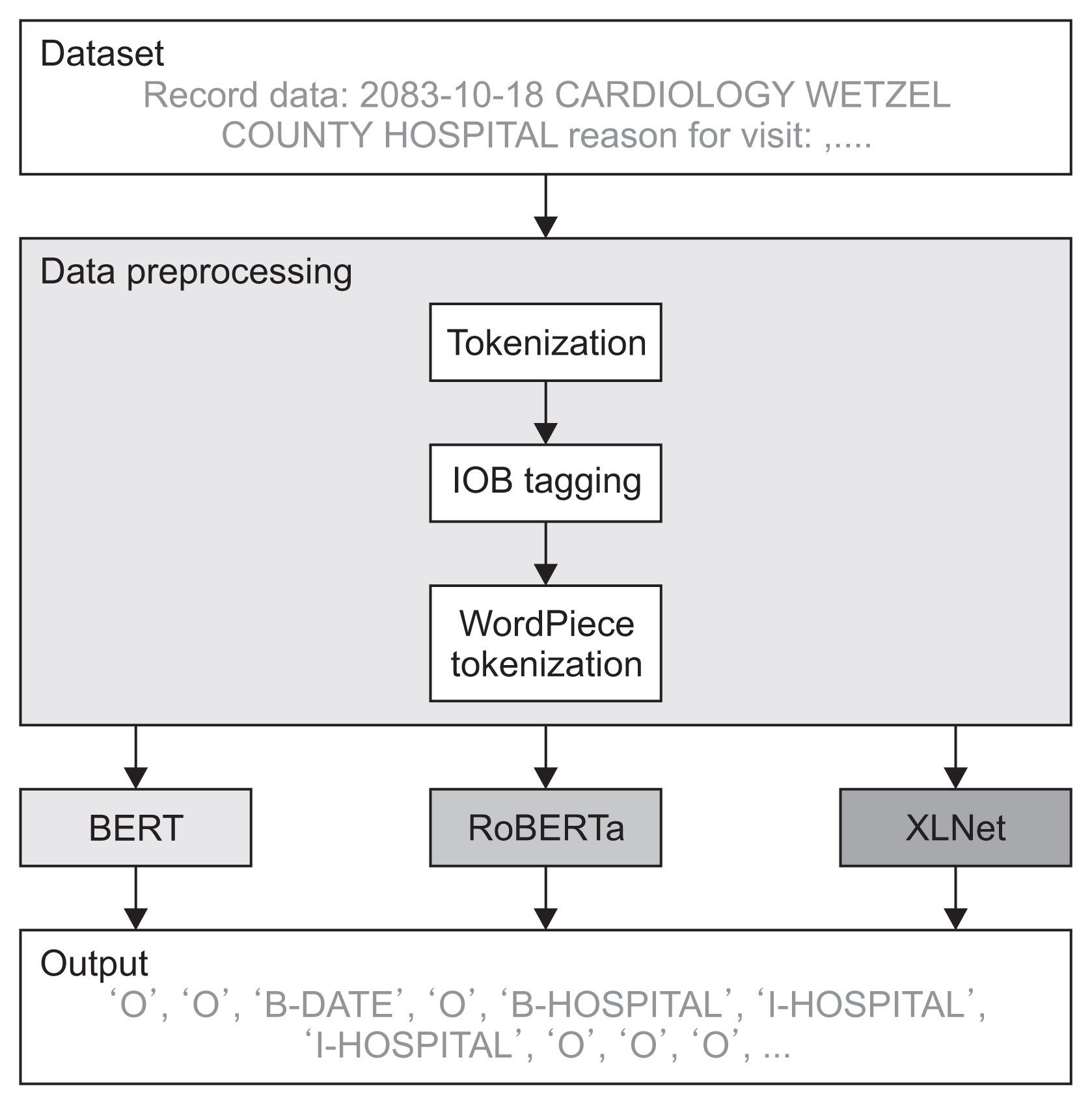
Figure 2
Model structure of BERT (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers).
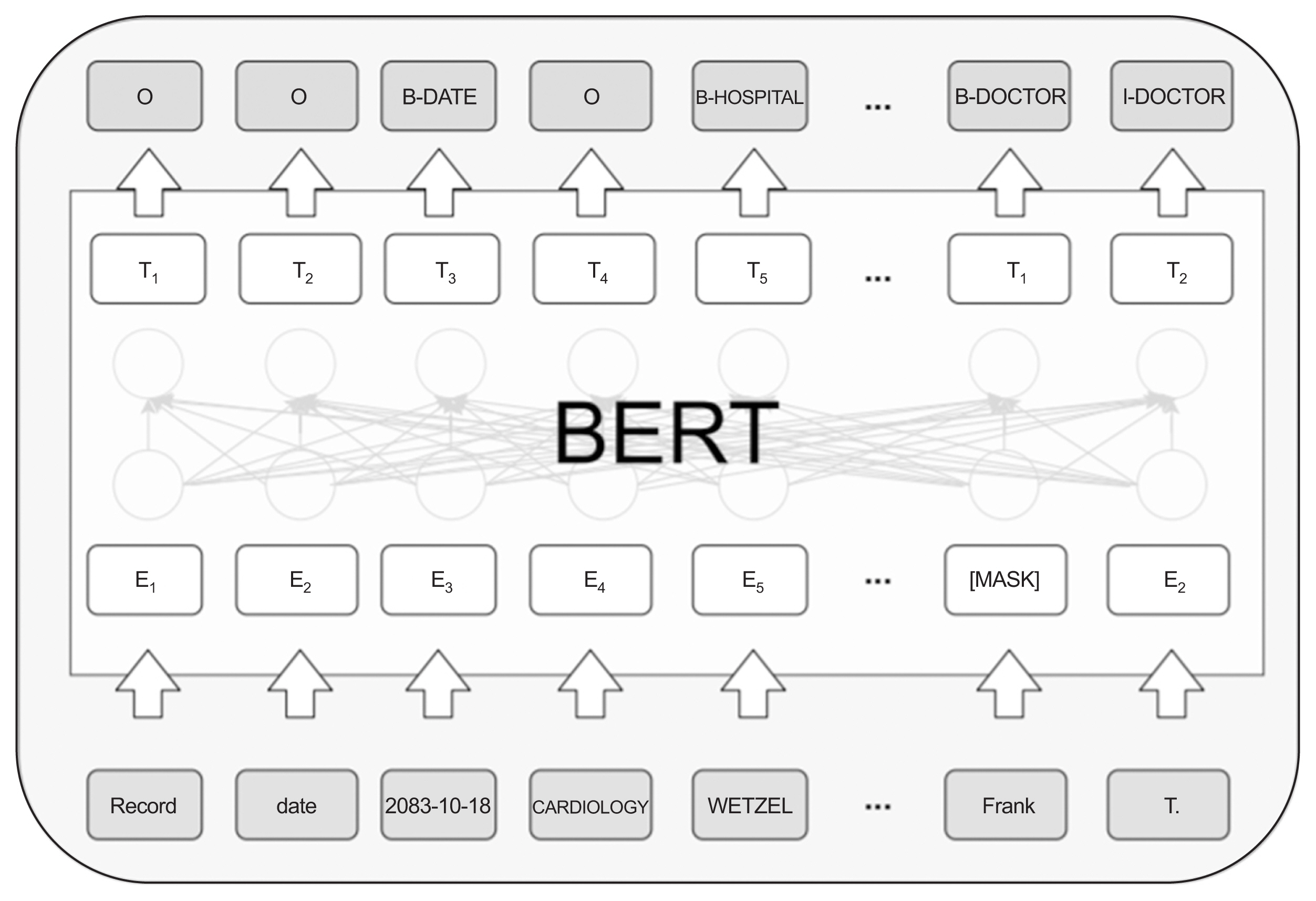
Figure 3
Permutation model with autoregressive and autoencoding models.
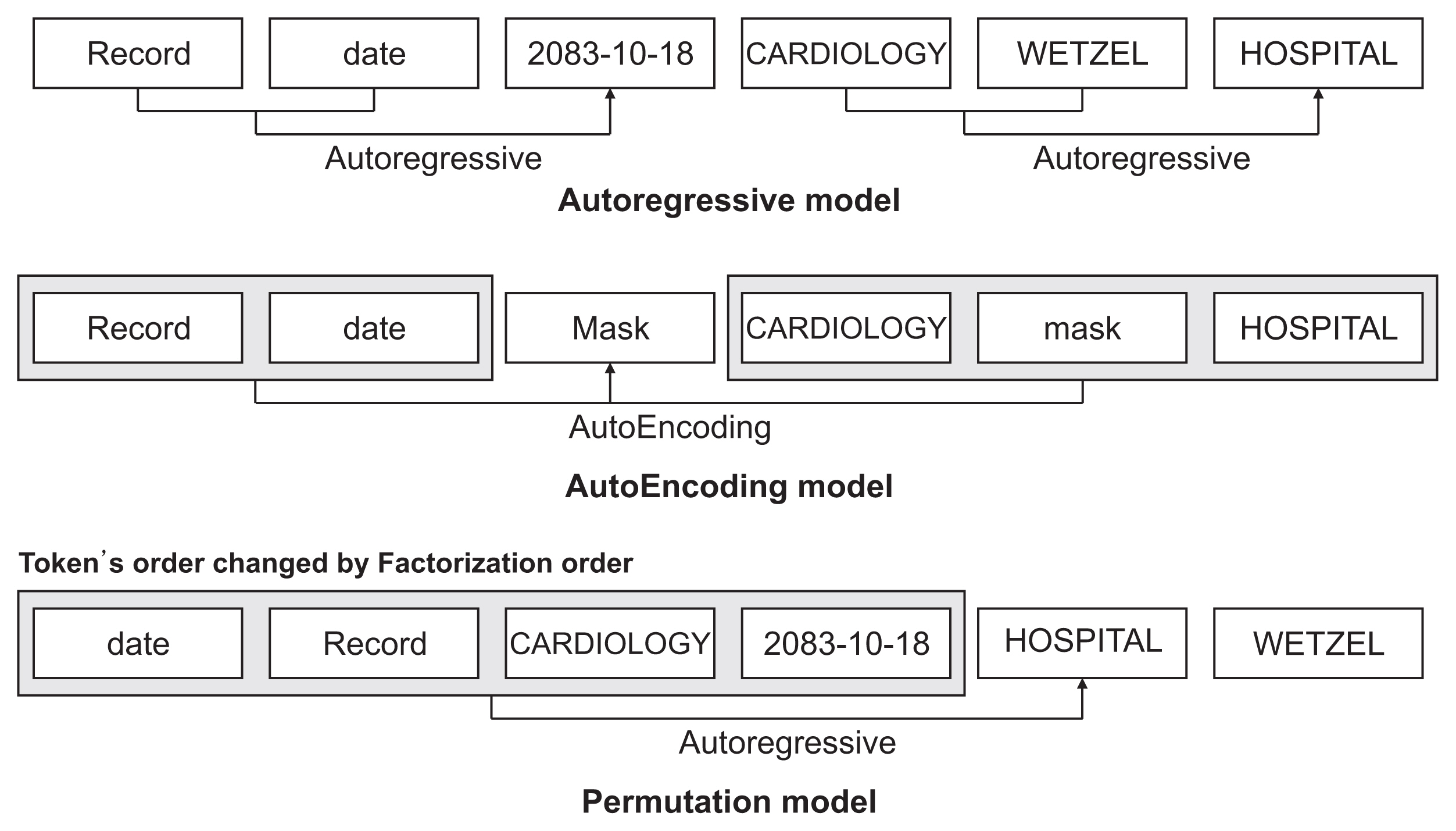
Table 1
Recall, precision, and F1-score of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet
|
Recall |
Precision |
F1-score |
|
BERT |
0.85 |
0.86 |
0.85 |
|
RoBERTa |
0.92 |
0.93 |
0.93 |
|
XLNet |
0.95 |
0.96 |
0.96 |
Table 2
Training time of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet
|
Training time (s) |
|
BERT |
348 |
|
RoBERTa |
685 |
|
XLNet |
1,215 |
Table 3
PHI entity performance evaluation of BERT, RoBERTa, and XLNet
|
Recall |
Precision |
F1-score |
Support |
|
BERT |
RoBERTa |
XLNet |
BERT |
RoBERTa |
XLNet |
BERT |
RoBERTa |
XLNet |
|
MEDICALRECORD |
0.97 |
0.98 |
0.99 |
0.98 |
0.95 |
0.98 |
0.98 |
0.96 |
0.98 |
1,849 |
|
DATE |
0.98 |
0.99 |
0.99 |
0.98 |
0.99 |
0.99 |
0.98 |
0.99 |
0.99 |
13,251 |
|
IDNUM |
0.93 |
0.91 |
0.93 |
0.88 |
0.75 |
0.88 |
0.90 |
0.82 |
0.90 |
642 |
|
AGE |
0.94 |
0.97 |
0.97 |
0.85 |
0.95 |
0.98 |
0.89 |
0.96 |
0.98 |
628 |
|
PHONE |
0.91 |
0.84 |
0.95 |
0.75 |
0.79 |
0.97 |
0.82 |
0.81 |
0.96 |
707 |
|
ZIP |
0.88 |
0.95 |
0.99 |
0.75 |
0.96 |
0.97 |
0.81 |
0.95 |
0.98 |
377 |
|
STATE |
0.68 |
0.92 |
0.94 |
0.92 |
0.58 |
0.88 |
0.78 |
0.71 |
0.91 |
248 |
|
PATIENT |
0.49 |
0.90 |
0.97 |
0.53 |
0.88 |
0.96 |
0.51 |
0.89 |
0.97 |
2,135 |
|
DOCTOR |
0.57 |
0.91 |
0.95 |
0.44 |
0.91 |
0.96 |
0.50 |
0.91 |
0.96 |
2,562 |
|
HOSPITAL |
0.31 |
0.85 |
0.90 |
0.32 |
0.73 |
0.81 |
0.31 |
0.78 |
0.85 |
1,539 |
|
CITY |
0.11 |
0.80 |
0.82 |
0.69 |
0.58 |
0.66 |
0.19 |
0.67 |
0.73 |
390 |
|
STREET |
0.13 |
0.93 |
0.95 |
0.12 |
0.90 |
0.89 |
0.12 |
0.92 |
0.92 |
183 |
|
COUNTRY |
0.00 |
0.12 |
0.61 |
0.00 |
0.92 |
0.81 |
0.00 |
0.21 |
0.73 |
122 |
|
DEVICE |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
29 |
|
LOCATION-OTHER |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
15 |
|
ORGANIZATION |
0.00 |
0.07 |
0.45 |
0.00 |
0.40 |
0.71 |
0.00 |
0.12 |
0.55 |
92 |
|
PROFESSION |
0.00 |
0.47 |
0.51 |
0.00 |
0.33 |
0.54 |
0.00 |
0.39 |
0.53 |
136 |
|
USERNAME |
0.00 |
0.89 |
0.95 |
0.00 |
0.88 |
0.79 |
0.00 |
0.89 |
0.86 |
148 |
Table 4
Examples of comparisons of valid and prediction tags in BERT
|
Instances |
|
Sentences |
pain |
persisted |
even |
after |
returning |
from |
blounstown |
|
Valid tags |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘B-CITY’ |
|
Prediction tags |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘O’ |
‘B-HOSPITAL’ |
References
3. Seong D, Yi BK. Research trends in clinical natural language processing. Commun Korean Inst Inf Sci Eng 2017;35(5):20-6.

6. Shin SY, Park YR, Shin Y, Choi HJ, Park J, Lyu Y, et al. A de-identification method for bilingual clinical texts of various note types. J Korean Med Sci 2015;30(1):7-15.


7. Lafferty J, McCallum A, Pereira FC. Conditional random fields: probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML); 2001 Jun 28–Jul 1. San Francisco, CA; p. 282-9.

8. Wang Y. Annotating and recognising named entities in clinical notes. Proceedings of the ACL-IJCNLP 2009 Student Research Workshop; 2009 Aug 4. Suntec, Singapore; p. 18-26.

9. Dreyfus SE. Artificial neural networks, back propagation, and the Kelley-Bryson gradient procedure. J Guid Control Dyn 1990;13(5):926-8.

11. Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 1997;9(8):1735-80.


13. Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2013 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781

14. fastText [Internet]. Menlo Park (CA): Facebook Inc.; 2020 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://fast-text.cc/

15. Peters ME, Neumann M, Iyyer M, Gardner M, Clark C, Lee K, et al. Deep contextualized word representations [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2018 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05365

16. Kim JM, Lee JH. Text document classification based on recurrent neural network using word2vec. J Korean Inst Intell Syst 2017;27(6):560-5.

19. Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2018 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805

20. Lan Z, Chen M, Goodman S, Gimpel K, Sharma P, Soricut R. ALBERT: a lite BERT for self-supervised learning of language representations. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR); 2020 Apr 26–30. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.

21. Liu Y, Ott M, Goyal N, Du J, Joshi M, Chen D, et al. ROBERTa: a robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2019 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692

23. Kingma DP, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2014 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980

24. Yang Z, Dai Z, Yang Y, Carbonell J, Salakhutdinov RR, Le QV. Xlnet: generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2019;32:5754-64.

28. Kingma DP, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational bayes [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2013 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114

29. Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2014;27:2672-80.

30. Alsentzer E, Murphy JR, Boag W, Weng WH, Jin D, Naumann T, et al. Publicly available clinical BERT embeddings [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org; 2019 [cited at 2022 Jan 10]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.03323